
Accessibility in SEO: Why you should optimise for everyone

Website accessibility is extremely important as it plays a big role in the experience for online users, and a poor user experience leads to big issues for your SEO. But what exactly is web accessibility?
Well put simply, it’s ensuring that websites and online content are designed and still functional for those with disabilities. Thus ensuring that websites have equal access and usage for any type of users.
Why does accessibility matter and how can it affect your SEO?
Well, the main reason is that ensuring everyone has equal access to places both offline and online is a legal requirement, and there are many governing bodies out there that regulate this. For example, in the UK there is the British Standard Institution (BSI) and the Equality Act of 2015, whilst in America there is the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
As well as the legal side of things, another key reason is user experience. If websites aren’t providing a good user experience or any experience for all its possible users, then they’re losing out on potential customers. User experience is a key factor for search engines to know how to rank your site, and therefore if you want your SEO efforts to be rewarded then don’t forget about accessibility.
But does accessibility affect SEO?
It’s simple really- if your website doesn’t give your users what they need, then they’re not going to stick around, they’re going to leave. It’s even been found that 88% of users who have a bad website experience won’t return. Websites that can’t keep visitors aren’t trusted or ranked highly by Google. This is why businesses need to keep track of their engagement rate and other metrics in Google Analytics, to understand how users are interacting with their site.
Another factor that can impact your rankings is Google’s Core Web Vitals(CWV). This report shows how your website performs in the real world and takes into account metrics that can again impact your user experience such as how long it takes your pages or content to load. It’s important to note that implementing accessibility features incorrectly can cause issues for your CWV and therefore your SEO strategy.
For example, too many headings or too much alt text that are irrelevant and don’t add any value might only add confusion, which can have a negative affect on SEO- it’s possible that this can disrupt a positive user experience and damage your rankings.
So how can you make a website more accessible and not impact your SEO strategy?
Understanding the principles of accessibility
First things first, you need to understand there are four main principles of web accessibility that use the acronym POUR:
- Perceivable – ensuring that all users can perceive a website. This means making content accessible for those with sight or hearing problems.
- Operable – making a website easy to navigate and usable for all users with disabilities and not just relying on everyone using a keyboard or mouse.
- Understandable – can users read and comprehend your content? Think about clear and direct language and display it in an easily readable manner.
- Robust – Is your website compatible with assistive technology that users may need? For example, a visually impaired person may need to use a screen reader.
Now you understand the four key principles, it’s time to improve the accessibility of your website, whilst also enhancing your SEO strategy.
Making a website more accessible
There are many ways to make a website more user-friendly; we’ve broken them down into this easily-to-implement list.
- Clear layout and consistent layout – A good accessible website is easy for a user to understand and navigate. Think about clear headings, a logical process and such features as breadcrumbs that allow users to go back the way they came.
- Descriptive titles – ensure your users quickly know what your content is about by using relevant page titles.
- Give your content structure – As well as relevant page titles, your content should also have an easy-to-follow structure and utilise appropriate headings.
- Have a sitemap – Not only are sitemaps important to search engines to understand, coral and index your site, but they can also help users navigate around.
- Use meaningful anchor text – When adding links to your content you need to ensure the text which is displayed for those links actually ‘links’ to what it says it is.
- Add alt text to images – Again this is beneficial to both search engines and users as it is text which describes your imagery for those users who can’t see pictures clearly.
- Ensure readability – How easy is it for users to read your content? This is where legible fonts, contrasting colours and white space on a website come into play.
- Include transcripts and captions – using video content is another way you can make your content accessible enabling users with visual impairments to be able to hear content, but then you also need to ensure that your video content can be understood by those who can’t hear sound.
- Make interactive elements easy to understand – if your website has a lot of interactive content then you need to make sure it’s clear to all users how they can interact to get the most out of it.
Now you’ve added some functionality, it’s time to test your accessibility.
Testing your website accessibility
There are many tools out there that can help you assess how accessible your website is. To help you on your way, we thought we’d share a few.
Google Lighthouse
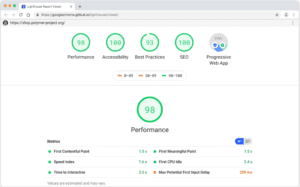
Google Lighthouse is an open-source tool that aims to improve the performance and quality of websites. The tool works by a user inputting a URL and the tool creating a report that scores you out of 100 for a range of metrics including accessibility.
You can even choose to run the report for desktop and mobile, ensuring that your website is accessible and optimised for different devices.
WAVE
WAVE is a suite of tools that can help you make your website more accessible. Like Lighthouse, you can input a URL and a report is generated that shows errors such as skipped heading levels, suspicious alt text and low contrast. The report will also detail positive accessibility features.
BrowserStack
BrowserStack offers a free trial but ultimately is paid for, and that’s due to the wide range of testing abilities it provides. As well as testing accessibility and ensuring your website is compliant, you can even check it across different browsers and other things such as debugging and app testing.
Conclusion
Now perhaps you’re thinking this sounds like a lot of extra work and is it really necessary? However, we need to remember that the internet is for everyone and therefore you shouldn’t play a part in restricting its use. Start off by assessing where your website currently stands and then work with UX designers and web developers to make changes over time that can make a big difference.
