Google Knowledge Graphs are one of the most notable changes in a long line of updates, tackling the way search engines organise and deliver information to users.
Along with the Helpful Content Update, Google’s Knowledge Graphs are designed to make search more ‘universally accessible and useful’ – even if they’ve been knocking around for nearly fifteen years.
The knowledge graph visually shows how Google answers a query, by pulling on data-entity relationships and presenting what it deems relevant to the user journey.
For more information on how to implement the right structured data for getting a knowledge panel, speak to our SEO experts today.
In a nutshell: the Knowledge Graph gives users quick and clear answers to their questions, especially on real-world topics.
These topics, also known as entities, can be anything from:
- People
- Organisations
- Places
- Events
- Things
- Animals
- Foods
- Abstract concepts
It also looks at relationships, which deals with how these different topics might relate to one another – another facet of network science.
For example, let’s look at the Google Graph Entry for Alan Turing:

This search doesn’t provide just straightforward, standard results from top-ranking websites. Instead, it provides colour to the search, through a summary of the basic information about the author, his notable work, and other relevant media.
This means no more scrolling through endless text to find what you’re looking for, or typing and retyping your query to find the right answer – just speedy answers where, and when, you need them.
All this from just a small section of Google’s Knowledge Graph.
It’s an approach that suits the searcher, search engine, and SEO-savvy businesses looking to increase their visibility.
In this blog, we’ll take a closer look at Google’s Knowledge Graph, alongside its impact on SEO and what it means to optimise your website for it.
Let’s get started.
How does it work?
Google first introduced the Knowledge Graph in 2012, using the slogan “things, not strings.”
Far from just a catchy slogan, Google intends to understand the meaning of topics in the real world and their relationships – rather than serving up results based on the words used in search queries.
Imagine the Google Knowledge Graph as a mind map. Relationships between entities are represented by nodes, and entities are represented by edges, so when you google Alan Turing you might end up with related links to:
- The Enigma Code – Turing was the lead codebreaker
- Bletchley Park – The principle centre of Allied code breaking
- Computer science – Turing was a pioneer in modern computer science, as well as mathematician, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist, according to Google.
- Apple Logo – Turing took his life with a cyanide-laced Apple, which is now the symbol of the famous technology brand.
Thanks to this database of knowledge, Google is able to provide immediate answers to search queries like “famous computer scientists” with Alan Turing listed.
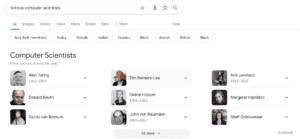
Even if Turing isn’t explicitly mentioned, Google understands the context and knows which queries are likely to be related to him—thanks to the information in the Knowledge Graph.
So where is this information collected from? For the graph, Google collates data from a variety of sources, like Wikipedia, Wikidata, and the CIA World Factbook.
The information Google shows in the search results is generated automatically.
How Google showcases this information
The knowledge graph takes four main forms on the search results pages, with each one impacting how it appears depending on user behaviour.
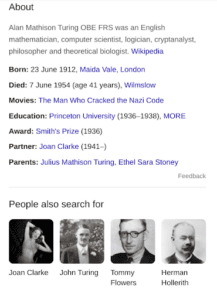
Knowledge Graph Sidebar
The Knowledge Graph sidebar is the most recognisable and contains the largest amount of information, found on the right-hand side of the page.
It can answer a user’s query without them having to click on a search result and does not impact how results are pushed below the fold.
Quick answer box
These tend to appear when it’s clear from the search what exactly is being asked by the user.

See? It’s pretty self-explanatory.
Knowledge graph customised answer
These appear on top of the organic listings and take potentially hundreds of different forms depending on the topic. Google has been getting rather creative with these, offering visual tabs for searches like:
- Football results, Formula One standings and league tables
- Flight listings and train times
- Weather reports
Extended instant answer
This is a longer answer to a user’s question, made up of an extended snippet of text from a website. As they can be much longer and detailed, accommodating them might mean that organic search results are pushed lower on the page. They can appear as ‘floating quotes’, numbered bullets or even step-by-step instructions.
These snippets often contain a link to the original content, giving searchers the chance to click-through and view the original piece.
How the this impacts SEO
Although it can be tricky to get one, if your business has a knowledge panel, you get automatic increased visibility in SERPs – thanks to snippets and images that Google thinks is relevant.
However, that doesn’t immediately create an uptick in clicks. In fact, because Google offers answers to users directly on its results pages, zero-click searches have increased.
These are the searches that don’t end up with a user clicking a result, as everything the audience needs is plain to see on-page.
A Semrush study from 2022 found that around 25% of all desktop searches are zero-click searches.
But, there are some benefits to Google Knowledge Graphs.
Brand awareness
Unlike a SERP featured snippet, it’s unlikely that getting a shout-out in the instant answer box will go the extra mile for your SEO traffic.
But, getting referenced by Google as an authoritative source of information is a great way to boost your brand, especially in the eyes of the E-E-A-T algorithm. In short, if your website is seen to be a place where Google, of all places, is getting its information from, it nabs a brand credibility signal.
The result? Your content is more likely to be put in front of your target audience, which certainly doesn’t hurt.
But what can you do to keep considering Google’s Knowledge Graph in your SEO campaigns?
We’ll touch on this next.
Keyword research
During your keyword research, make sure to check how some of the more heavily searched keywords are impacted by knowledge graph results.
Although there are no tools that currently provide this information – it needs to be collected manually. However, it still might be worth the time, as targeting a key phrase that the knowledge graph might pick up on will reduce the impact of your organic search results.
Essentially, when in doubt: check!
For more top tips, check out this video from our very own Organic Lead, Amy Leach.
Analytics adjustments
A new Extended Instant Answer box appearing on a SERP for a key question can have an impact on the amount of traffic you can get.
To counter it, add an annotation in Analytics and make sure everyone in the campaign understands the reasons why a web-page at position 1 is only receiving a portion of its expected traffic.
It’s usually down to being pushed below the fold by a high-quality instant answer box.
Unanswered questions
While the Knowledge Graph often provides an answer to many short-form queries, in many cases more information is needed to give the searcher context.
Understanding which elements of the users’ questions are not being answered by the Knowledge Graph can be a useful benchmark for optimising landing page content. This can help you capture searchers who aren’t satisfied by the knowledge graph answer shown.
Key Takeaways
- In the search results, Google’s Knowledge Graph provides answers to some questions directly, based on a huge database of information about search queries
- In search results, Knowledge Graph data is most frequently displayed in knowledge panels
- Google requires you to demonstrate your reputable status and help them understand your business in order to optimise Knowledge Graph
- Structured data is essential for getting a knowledge panel, as is having links from other credible sources
If you’re interested in how Embryo could transform your digital campaigns across SEO, PPC, Social, Digital PR and more – get in touch today to speak to a member of the team.
FAQs
Answered by Amy Leach
How are Google knowledge graphs different to rich snippets?
Google Knowledge panels tend to appear on the right-hand side of the SERP and usually collate information from different sources. Rich snippets are shown at the top of the SERP, where key information taken from the top ranking page is shown, decreasing the need to click on a link to find that information.
Do Google knowledge graphs impact SERP visibility?
Knowledge panels shouldn’t impact the links that show on the SERP. Google knowledge graphs may however take up a large space on the SERP, moving pages further down.
How many people click on the first SERP result?
The #1 search result on Google has an average click-through rate of 27%
Is the information presented in Knowledge graphs manually checked?
This is an automated process by Google. Knowledge graph creation will have certain strict criteria so that data is presented correctly and for relevant searches.
Will only informational content help to get my website featured in a knowledge graph?
Knowledge graphs mostly focus on factual content which isn’t likely to date quickly.












